
Master Photorealistic Rendering for Architecture, Interior Design & 3D Visualization!
This course provides a comprehensive introduction to V-Ray, one of the most powerful rendering engines used in architecture, interior design, and 3D visualization. Learn how to create high-quality, photorealistic renders using industry-standard software like 3ds Max, SketchUp, and Rhino.
By the end of this course, you'll have the skills to produce stunning visualizations for architectural presentations, product designs, and animations.
This course is ideal for:
Upon successful completion, students will receive a Certificate in V-Ray Rendering, validating their skills in high-quality rendering and visualization.
V-Ray is a high-quality, photorealistic 3D rendering software developed by Chaos Group. It is widely used by artists, designers, architects, and animators to create stunning and realistic images, animations, and visualizations. V-Ray integrates seamlessly with many 3D modeling programs, such as SketchUp, 3ds Max, Maya, Rhino, and Revit, making it a popular choice for a wide range of industries.
Photorealistic Rendering: V-Ray is known for its ability to produce highly realistic images and animations. It uses advanced rendering techniques like ray tracing to simulate how light interacts with objects in the real world, producing realistic shadows, reflections, and textures.
Compatibility with Multiple 3D Software: V-Ray works with a variety of 3D modeling and CAD software, including:
Real-Time Rendering: V-Ray offers V-Ray RT (Real-Time), which allows users to see live feedback on changes they make to the scene. This feature enables a more interactive workflow, especially when making adjustments to materials, lighting, or camera angles.
GPU and CPU Rendering: V-Ray supports both GPU (graphics card) and CPU (central processing unit) rendering, allowing you to choose the best rendering option based on your hardware setup. GPU rendering can be significantly faster, especially with powerful graphics cards, while CPU rendering can provide more stability in complex scenes.
Global Illumination: V-Ray excels at simulating realistic lighting conditions through Global Illumination (GI). This technique models how light bounces off surfaces in a scene, adding depth and realism to renders. V-Ray includes several GI methods, such as Irradiance Map and Brute Force, to suit different scenes.
Material and Texture Libraries: V-Ray comes with an extensive library of materials and textures that you can use to create realistic surfaces. These materials include settings for things like reflections, refractions, and bump mapping, which simulate real-world materials like glass, metal, wood, and fabric.
Advanced Camera Effects: V-Ray features a set of advanced camera effects like depth of field, motion blur, and lens effects to simulate the behavior of real-world cameras. These effects can help achieve a cinematic look in renders.
Network Rendering: V-Ray supports distributed rendering (DR), which allows multiple computers (nodes) to work together on a single render job, speeding up rendering times and making the process more efficient.
Post-Processing Effects: After rendering, V-Ray includes a frame buffer that allows you to adjust color balance, contrast, and other parameters without needing to go into post-production software like Photoshop. This makes it easier to fine-tune your images.
V-Ray for Animation: V-Ray can also render animations with a high degree of realism, including moving lights, cameras, and objects. It's commonly used in creating architectural walkthroughs, animated visualizations, and product animations.
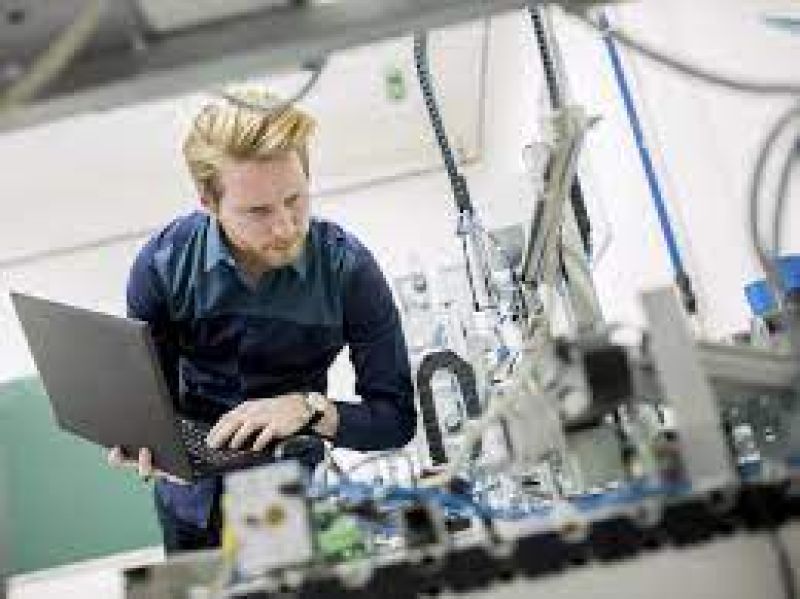
Architectural Visualization: V-Ray is highly popular in architecture and design, used to create photorealistic renderings of buildings, interiors, and landscapes. It helps architects and designers present their ideas in a visually compelling way to clients or stakeholders.
Product Visualization: V-Ray is often used by industrial designers and product designers to create realistic visualizations of products before they are manufactured. This includes everything from furniture to cars, electronics, and consumer goods.
Game Development: V-Ray is used to create realistic assets for video games. It helps game developers create high-quality textures, environments, and objects that can be used in game engines like Unity or Unreal Engine.
Animation and Film Production: V-Ray is used in the creation of CGI (computer-generated imagery) for movies, television, and commercials. It allows for the creation of lifelike environments, characters, and visual effects that are often indistinguishable from real life.
Interior Design: Designers use V-Ray to visualize interior spaces with high-quality materials, lighting, and textures. It can be used to simulate lighting conditions, furniture, and other interior elements, allowing clients to see what the space will look like before any work is done.
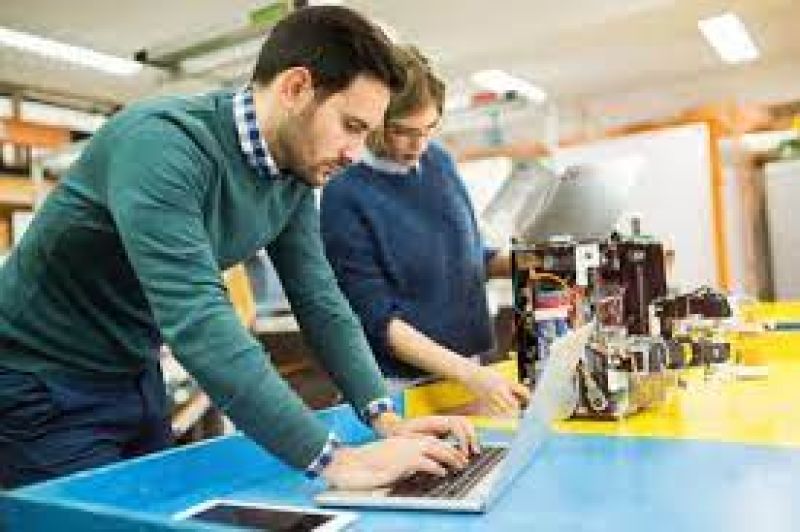
Model Creation: First, you create a 3D model using your preferred modeling software (such as SketchUp, 3ds Max, or Rhino). This model could be a building, a product, or a scene.
Apply Materials: Next, you apply materials to the objects in the scene. This could include textures like wood, concrete, metal, glass, and fabric. You can adjust material properties such as roughness, reflectivity, and bump maps.
Set Up Lighting: Lighting is crucial for achieving realism in V-Ray. You can use various types of lights, including direct lights (like the sun or artificial lights) and environment lights (such as HDRIs or image-based lighting). V-Ray also supports realistic natural lighting through its Global Illumination system.
Camera Setup: You’ll place cameras in the scene to frame your shots. V-Ray offers real-world camera settings, including focus distance, depth of field, and lens effects.
Rendering: Once everything is set up, you render the scene. V-Ray will process the lighting, materials, and camera effects to generate the final image. The rendering time can vary based on scene complexity and hardware, but with V-Ray's optimizations, the process is usually fast.
Post-Processing: After the render, you can use V-Ray’s frame buffer to tweak color grading, exposure, and other aspects of the image. You can also export the render to external programs like Photoshop for additional adjustments.
Download V-Ray: You can get the V-Ray trial or purchase the full version from Chaos Group's website. V-Ray is compatible with different 3D modeling software, so make sure you download the correct version for your software (e.g., V-Ray for 3ds Max, V-Ray for SketchUp).
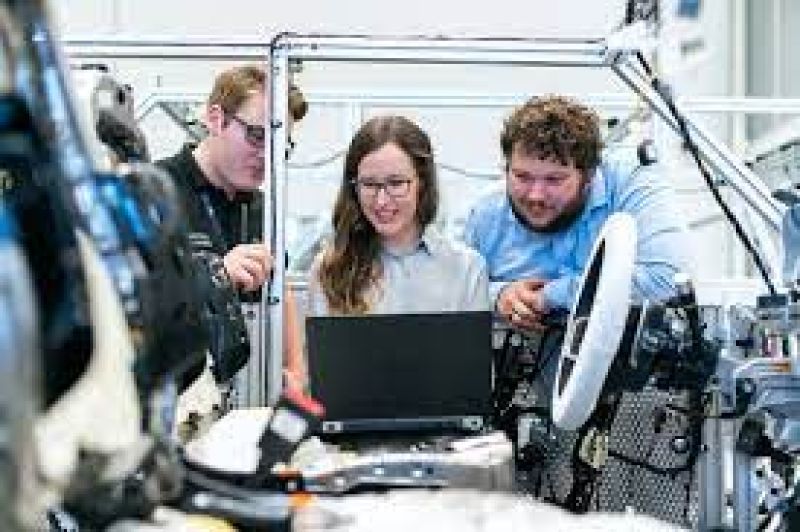
Learn V-Ray Basics: Start with learning how to apply basic materials, set up lighting, and render simple scenes. There are plenty of tutorials available on YouTube and Chaos Group’s website to help you get started.
Use V-Ray in Your Workflow: Once you’re comfortable with the basics, start integrating V-Ray into your day-to-day projects. Experiment with advanced lighting techniques, creating realistic materials, and using V-Ray’s camera and rendering settings to fine-tune your outputs.
Hardware Considerations: V-Ray can be demanding on hardware, especially during rendering. If you're working with large, complex scenes, ensure your system has a powerful CPU and GPU for faster processing. V-Ray supports GPU rendering for faster results using high-end graphics cards.
V-Ray is a versatile and powerful rendering tool used by professionals in architecture, design, animation, and product visualization. Its ability to produce photorealistic results, coupled with advanced features like real-time rendering and GPU support, makes it a go-to choice for anyone looking to create high-quality visualizations.

Course Code : S1 TALLY-01

Course Code : M-ADCA-01

Course Code : M-A1

Course Code : M-A2

Course Code : M-A3

Course Code : M-A4

Course Code : M-A5

Course Code : M-A6
Course Code : M-A7

Course Code : M-A8

Course Code : M-B1

Course Code : M-A9

Course Code : S-B 1

Course Code : C-DEO1

Course Code : S-B-12

Course Code : S-B-13

Course Code : C-CBA1
Course Code : S-B- 15

Course Code : S-B- 16
Course Code : S-B-18

Course Code : S-B- 17

Course Code : S-B- 19

Course Code : S-B- 20

Course Code : C-CR

Course Code : S-B- 22

Course Code : S-B- 23

Course Code : C-CTE1

Course Code : S-ADCA1

Course Code : M-ADCA1

Course Code : S-ADCA1

Course Code : C-DEO1

Course Code : M-D-MK01

Course Code : S-PCDM

Course Code : S-PCWD

Course Code : S-PCWD-1

Course Code : S-PCSD
Course Code : IT

Course Code : S-PCGD

Course Code : S-PCEAB

Course Code : S-CBSE

Course Code : S-CASE

Course Code : S-C-HN1

Course Code : M-D-DBM

Course Code : DCAD

Course Code : S-A-AX

Course Code : S-C -CHTML

Course Code : M-D-HTML

Course Code : M-D-BM

Course Code : M-D-DP

Course Code : S-C-JAVA

Course Code : S-C-BDP

Course Code : S-C-L3D

Course Code : S-C-PHP

Course Code : S-C-VRAY

Course Code : S-C-3DSMAX

Course Code : S-C-PTT

Course Code : S-C-PYT

Course Code : S-C-FD

Course Code : S-C-BFD

Course Code : S-C-CAD

Course Code : S-C-AP

Course Code : S-C-CM

Course Code : M-AD

Course Code : S-C-ITP

Course Code : S-C-IT

Course Code : S-C-OP

Course Code : S-C-DSD

Course Code : M-D-NTT

Course Code : S-C-FCA

Course Code : S-C-CA

Course Code : S-C-AE

Course Code : S-C-CC

Course Code : S-C-FM

Course Code : S-C-CFPWM

Course Code : S-C-NM

Course Code : S-C-CP

Course Code : S-C-JQUERY

Course Code : S-C-OOPU

Course Code : S-C-PHOTOSHOP

Course Code : S-C-BS

Course Code : S-C-FA

Course Code : S-C-CT

Course Code : M-DCAA

Course Code : S-C-ETSP

Course Code : S-CCA

Course Code : M-DCA

Course Code : M-C-AF

Course Code : C-CBA1

Course Code : M-ADCA1

Course Code : M-D-EL

Course Code : C-DEO1

Course Code : M-ADCA1

Course Code : C-CR
Course Code : D

Course Code : S-T-R 3D-MAX
Course Code : S-A

Course Code : M-AD

Course Code : S-C-BDP

Course Code : S-FITNESS

Course Code : M-FITNESS

Course Code : S-FITNESS

Course Code : M-EVENTM

Course Code : S-CCA

Course Code : C-CBA1

Course Code : M-ADCA1

Course Code : M-FASHIONDE

Course Code : M-YOGA

Course Code : S-YOGA

Course Code : C-DEO1

Course Code : C-CTE1

Course Code : S-CCA

Course Code : M-NTT1YEAR

Course Code : M-D-NTT

Course Code : M-ADCA1

Course Code : S-C-FD

Course Code : S-C-BFD

Course Code : S-CBMA

Course Code : S-TPHYTHON

Course Code : S-CCA

Course Code : S-TC-CHM

Course Code : M-MOBILEREPARING

Course Code : M-HSHC

Course Code : M-ECC

Course Code : M-D-COSMO

Course Code : M-NTT2YEAR
Course Code : M-ITI-WELDER
Course Code : M-ITI-ELECTRICIAN
Course Code : M-ITI-FITTER
Course Code : M-ITI-PLUMBER
Course Code : M-ITI-COPA
Course Code : M-ITI-HSI
Course Code : M-ITI-FIRESAFETY
Course Code : M-ITI-WIREMAN

Course Code : M-ITI-DRAUGHTSMAN

Course Code : M-ITI-CUTTING & TAILORING

Course Code : M-D-NTT

Course Code : C-DEO1

Course Code : M-D-NTT

Course Code : M-NTT2YEAR

Course Code : M-D-MK01
Course Code : S-CNA
Course Code : S-CNA

Course Code : S-CBMA

Course Code : M-NTT2YEAR
Course Code : S-HSHC
Course Code : S-HSHC

Course Code : S-A-AX

Course Code : S-CCA

Course Code : C-CBA1
Course Code : M-COOKERY
Course Code : M-COOKERY

Course Code : M-NTT2YEAR

Course Code : M-ADCA1

Course Code : S-CBMA

Course Code : C-CTE1

Course Code : M-ECC

Course Code : C-DEO1

Course Code : M-ADCA1

Course Code : C-DEO1

Course Code : C-CBA1

Course Code : S-B- 19
Course Code : M-ITI-PLUMBER

Course Code : S-C-BDP
Course Code : S-CIHS
Course Code : S-DHT
Course Code : M-DHT
Course Code : S-CICC
Course Code : S-CIAM
Course Code : S-CISC
Course Code : S-CIBSWT

Course Code : C-DEO1

Course Code : C-CBA1

Course Code : S-B- 19

Course Code : C-CR

Course Code : S-PCEAB
Course Code : S-CIWD

Course Code : M-HSHC
Course Code : S-CNA
Course Code : S-HSHC
Course Code : S-CIHS
Course Code : S-CICC
Course Code : S-CIAM
Course Code : S-CISC

Course Code : M-ADCA1
Course Code : S-CBAA
Course Code : S-CBAA
Course Code : S-CBAA
Course Code : S-CBAA
Course Code : S-HETG
Course Code : S-HETG

Course Code : C-DEO1

Course Code : M-ADCA1
Course Code : S-CPP
Course Code : S-CCM
Course Code : S-CIJM
Course Code : S-PHPMM
Course Code : S-CIPN
Course Code : S-CPWP
Course Code : S-DSAJC
Course Code : S-DBMSSQL
Course Code : S-CIGMP
Course Code : S-CIMSD
Course Code : S-SSBD
Course Code : S-DJGO
Course Code : S-LINX
Course Code : S-CIGG
Course Code : S-BTCSC
Course Code : S-DJGO
Course Code : S-LINX
Course Code : S-PHPMM
Course Code : S-CIBSWT
Course Code : S-CIWD

Course Code : S-CASE

Course Code : S-CBSE
Course Code : M-DIWC
Course Code : M-DIWC
Course Code : S-SSBD
Course Code : S-S-HAND_EMBRO_21
Course Code : M-M-M0002222
Course Code : M-DHT
Course Code : M-ECCE2YEARS
Course Code : M-ADECCE
Course Code : S-CPP

Course Code : S-CBMA
Course Code : S-CNA
Course Code : S-HSHC
Course Code : S-CIHS
Course Code : S-DHT
Course Code : S-CICC
Course Code : S-CIAM
Course Code : S-CISC
Course Code : M-ADFA

Course Code : M-ADCA1

Course Code : C-CBA1

Course Code : M-ADCA1
Course Code : S-CIBCWT(4MONTHS)
Course Code : M-DIHRBK
Course Code : M-ITI-ELECTRICIAN
Course Code : M-ITIELECTRICIAN1YEAR
Course Code : M-ITIELECTRICIAN1YEAR
Course Code : M-DCILS








